Cryptocurrencies emerged with promises of decentralization and anonymity that traditional financial systems couldn’t match. Bitcoin introduced a revolutionary concept: transactions without intermediaries, offering users privacy. But is crypto truly untraceable?
This perception of anonymity has attracted diverse users, from privacy enthusiasts to those with illicit intentions. As cryptocurrency adoption grows, understanding the actual privacy level these digital assets provide becomes crucial.
Government agencies have developed sophisticated tracking methods, challenging the notion of complete anonymity.
This post explores cryptocurrency traceability, tracking methods, and ways to enhance privacy in today’s evolving crypto landscape.
Let’s begin!
Is Crypto Traceable: Key Takeaways
- Most cryptocurrencies operate on public blockchains where every transaction is permanently recorded and visible to anyone, making them anonymous rather than anonymous.
- Government agencies like the IRS use sophisticated blockchain analysis tools to link cryptocurrency addresses to real-world identities, often through exchange data.
- Starting in 2026, all US crypto exchanges (including decentralized ones) will be required to report transaction data to the IRS through Form 1099-DA.
- While privacy coins and mixing services can enhance anonymity, they’re not foolproof, as demonstrated by several high-profile cases where “anonymous” crypto was successfully traced.
Understanding Blockchain and Transaction Transparency
Blockchain technology works like a public digital ledger that permanently records all cryptocurrency transactions. Unlike your bank statement, which is only visible to you, blockchain data is visible to everyone.
When you send crypto, your transaction joins others in a “block” that gets added to the chain. Each transaction shows who sent how much to whom and when.

This creates an important distinction — crypto addresses provide pseudonymity, not anonymity. Your Bitcoin address doesn’t show your name, but it acts like a consistent username that creates trackable patterns.
Using blockchain explorers (like Blockchair or Etherscan), anyone can view your entire crypto transaction history—seeing when you received or sent funds, how much was involved, who you’ve transacted with, and your current balance.
Many new crypto users don’t realize just how transparent their transaction activity actually is on public blockchains.
How Do Crypto Exchanges Work?
Cryptocurrency exchanges function as platforms where users can buy, sell, and trade digital assets. They serve as crucial on-ramps and off-ramps between traditional financial systems and the crypto ecosystem.
Most established exchanges operating in the United States are required to comply with financial regulations, including reporting certain information to tax authorities.
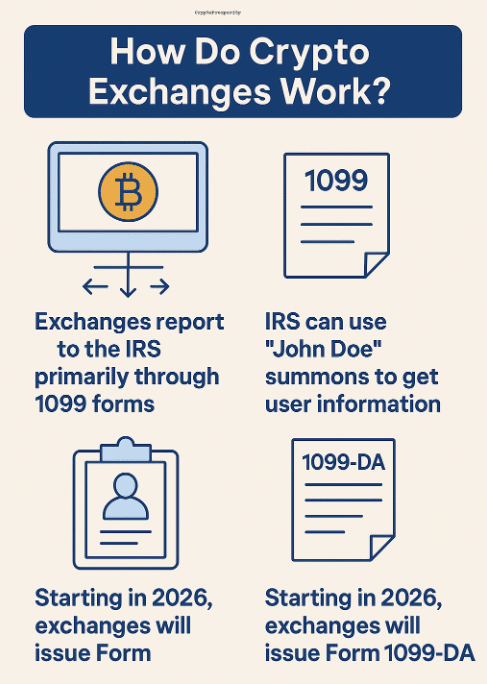
Exchanges report to the IRS primarily through 1099 forms, which detail transactions that might create taxable events. This reporting occurs because cryptocurrency is treated as property for tax purposes, meaning capital gains tax applies when you sell or exchange crypto at a profit.
Major exchanges comply with these requirements to maintain regulatory goodwill and legal operation status.
In addition, the IRS has not hesitated to issue “John Doe” summons to exchanges like Coinbase and Kraken, compelling them to provide information about users who meet certain transaction criteria, even without knowing specific identities in advance.
Starting in 2026, new regulations will require brokers (including exchanges) to issue Form 1099-DA to both users and the IRS, significantly expanding the government’s visibility into crypto transactions.
How Can Cryptocurrency Be Traced?
Cryptocurrency tracing involves several sophisticated techniques to follow the movement of digital assets across the blockchain. Despite the pseudonymous nature of transactions, several methods make tracing possible:
Blockchain analysis firms like Chainalysis and CipherTrace use advanced algorithms to identify patterns in transaction data. These tools can group multiple addresses that likely belong to the same entity—a technique called “clustering.”
When one address in the cluster is identified, all associated addresses become linked to that identity.
Users’ identities are most commonly revealed through exchanges that implement Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures.
Once you verify your identity on an exchange and withdraw funds to your wallet, that wallet address becomes connected to your real identity. Subsequent transactions from that wallet create a trail that can be followed.
Law enforcement agencies have become increasingly sophisticated in their tracking abilities. In 2021, the IRS launched “Operation Hidden Treasure,” explicitly targeting crypto tax evasion.
Their success in recovering funds from high-profile cases demonstrates these tracing methods’ effectiveness.
Crypto Exchanges That Don’t Report To The IRS
Some platforms still operate without collecting KYC information or reporting to tax authorities.
These include decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap, where users trade directly with smart contracts rather than through a centralized entity, and peer-to-peer platforms like Bisq and RoboSats that facilitate direct transactions between users.
Other exchanges like KuCoin and TradeOgre have historically maintained looser KYC requirements, though regulatory pressure is forcing changes across the industry. Many non-KYC platforms have transaction limits or restricted features, making them less practical for more significant transactions.
It’s important to note that using non-reporting exchanges doesn’t exempt you from tax obligations—it merely means the exchange isn’t automatically reporting your activity. The legal responsibility to report and pay taxes still falls on the individual user.
How Does The IRS Track Crypto?
The IRS employs multiple strategies to monitor cryptocurrency transactions and ensure tax compliance. Their capabilities have expanded significantly in recent years with increased funding and specialized training.
The agency collaborates with blockchain analytics companies like Chainalysis to trace transaction patterns and identify potential tax evaders. These tools allow them to follow the flow of funds across multiple wallets and exchanges, even when attempts are made to obscure the trail.
Additionally, the IRS uses data from 1099 forms submitted by exchanges, matching this information against tax returns to identify discrepancies. They’ve also added a specific question about cryptocurrency transactions on Form 1040, creating a legal obligation to disclose crypto activity.
In 2022, the IRS received an $80 billion budget increase, allowing them to hire approximately 87,000 new agents, with cryptocurrency compliance specifically identified as a priority area.
This investment demonstrates the government’s commitment to ensuring cryptocurrency users meet their tax obligations.
Can the IRS Track Crypto From Anonymous Accounts?
The IRS can track cryptocurrency from supposedly “anonymous” accounts through various technical means. Although wallet addresses don’t explicitly contain personal information, the IRS has developed sophisticated methods to link these addresses to real identities.
One primary method involves following transaction chains. When you transfer crypto between an “anonymous” wallet and an exchange where you’ve completed KYC verification, that link creates a connection to your identity. The IRS can then use this connection to trace your other crypto activities.
Examples:
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of these techniques. In 2020, the IRS successfully tracked Bitcoin transactions related to a Twitter hack that affected numerous high-profile accounts.
Despite the hackers’ attempts to maintain anonymity, authorities traced the Bitcoin payments through the blockchain to identify the perpetrators.
Another notable case involved the recovery of $2.3 million in Bitcoin paid during the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack in 2021.
The FBI tracked the ransom payment through multiple wallets by analyzing transaction patterns on the blockchain, eventually identifying the addresses holding the funds.
These cases illustrate that while cryptocurrency wallets may appear anonymous, sophisticated analysis can often pierce this veil of anonymity, especially when users make common mistakes like reusing addresses or connecting to KYC-verified services.
Legal and Regulatory Implications in Crypto
Cryptocurrency regulations are evolving globally with significant privacy implications. Key agencies like FinCEN and FATF require exchanges to implement AML and KYC measures, verifying user identities and monitoring suspicious transactions.
The “Travel Rule” mandates sharing sender and recipient information for larger transactions. For individuals, this means increased scrutiny and detailed tax reporting. In the US, crypto is treated as property, requiring capital gains reporting on all transactions.
Businesses face even stricter requirements, including compliance programs and potential licensing based on services offered.
Can You Hide Your Cryptocurrency from the IRS?
Attempting to hide cryptocurrency from the IRS is both risky and illegal. Cryptocurrency tax evasion is considered a felony that can result in up to five years in prison, fines up to $100,000, plus prosecution costs.
Even if you use privacy coins, mixers, or non-KYC exchanges, the IRS has increasingly sophisticated methods to detect unreported crypto transactions. As blockchain analysis tools improve, transactions previously thought untraceable become vulnerable to investigation.
The IRS has specifically targeted crypto tax compliance in recent years, sending thousands of warning letters to suspected crypto holders who may not have properly reported their transactions.
With increased funding and enforcement resources, the agency is well-equipped to pursue cases of deliberate tax evasion.
Rather than attempting to hide assets, cryptocurrency users should focus on legitimate tax strategies like tax-loss harvesting, long-term holding for lower capital gains rates, or investing through tax-advantaged accounts where possible.
How To Strengthen Your Cryptocurrency Privacy?
While perfect anonymity is challenging to achieve, several methods can enhance your cryptocurrency privacy.
Privacy-focused cryptocurrencies like Monero use technologies such as ring signatures, stealth addresses, and confidential transactions to obscure transaction details, making them significantly more private than Bitcoin.
Coin mixing services, also known as tumblers, combine your coins with others’, making it difficult to trace the origin of any specific coin. Services like Wasabi Wallet and Samourai Wallet offer CoinJoin functionality that can enhance Bitcoin privacy.
However, some exchanges now flag coins that have gone through mixers, potentially creating complications when you try to cash out.
Privacy wallets provide enhanced security features, such as avoiding address reuse, which prevents observers from linking your transactions together.
Using the Tor network when accessing cryptocurrency services can also help mask your IP address, preventing this metadata from being linked to your transactions.
It’s important to note that while these methods increase privacy, they operate in legal gray areas in some jurisdictions. Due to regulatory concerns, some exchanges and services may refuse transactions from private coins or mixed coins.
The Future of Crypto Tracing and Privacy
The way cryptocurrencies are tracked and kept private is constantly changing. Advanced tools now use machine learning to better trace transactions, but at the same time, new privacy technologies are being developed to counteract this.

Some solutions, like Bitcoin’s Lightning Network, can improve privacy by handling transactions off the main blockchain. Other technologies, such as zero-knowledge proofs, offer privacy without slowing down the system.
There is an ongoing debate about privacy and security. While users want financial privacy, governments need to prevent crime and ensure taxes are paid.
Quantum computing could shake things up by breaking current security methods, but it might also lead to even better privacy protections. In the future, the battle between tracking and privacy tools is expected to continue.
Related Reads:
Conclusion: Crypto Is Traceable by IRS
Cryptocurrency balances privacy and transparency. While all transactions are recorded on the blockchain, tools exist to obscure identities—but achieving full anonymity is very difficult.
Government agencies, including the IRS, have advanced methods to track crypto transactions, especially when users interact with regulated exchanges. Most crypto activity can be traced, making compliance with tax laws essential.
The best approach is to follow legal requirements while using privacy tools to protect financial data. As the crypto world evolves, finding the right balance between privacy and regulation will remain a challenge.
Before using crypto, research the privacy risks of different platforms and consider seeking legal or tax advice to ensure compliance.
FAQs
Your wallet address can be linked to your identity through KYC-verified exchanges, blockchain analysis, and transaction patterns. Even non-custodial wallets can be connected to your identity when combined with other data points like IP addresses or exchange withdrawals.
The IRS expects you to track and report your cryptocurrency’s original acquisition price, which they may verify against exchange reports or your previous tax returns. Deliberately misreporting cost basis is considered tax fraud and can trigger audits extending back up to six years.
The IRS can track NFTs just like other cryptocurrencies since transactions occur on public blockchains. NFT purchases, sales, and trades create taxable events that should be reported and can be linked to identifiable wallets and exchanges.
The IRS can audit you for crypto activities within three years of filing, or six years if you’ve substantially underreported income. For suspected fraud cases, there’s no time limitation on when the IRS can investigate your crypto transactions.
File amended returns (Form 1040X) for those years within the three-year window from your original filing date. For deliberate underreporting, consider using Form 14457 for voluntary disclosure to potentially reduce penalties.
Report crypto transactions on Form 8949 and Schedule D, including the dates, cost basis, proceeds, and resulting gains or losses. Income from mining, staking, or payment for services should be reported as ordinary income on Schedule 1.

![Top 15 Crypto Podcasts to Listen to in 2025 [Popular]](https://crypto.prosperityforamerica.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Best-Podcasts-on-Cryptocurrency-1024x536.png)




